App Privacy Concerns: Understanding and Protecting Your Personal Information
In today’s digital age, mobile applications are an integral part of our daily lives, offering convenience and a wide range of services. However, as we become more reliant on these apps, there are increasing concerns about privacy and how our personal data is handled. Understanding the potential risks and knowing how to protect your information is essential to ensuring your privacy stays intact while using apps.

The Growing Concern of App Privacy
Apps have access to vast amounts of personal data, from your location and contacts to your browsing habits and payment information. While many apps require certain permissions to function properly, some request access to data that seems unnecessary for their core functions. This has raised serious questions about how companies use, store, and sometimes share our information.
In 2024, studies show that over 80% of mobile apps request access to personal data, even if it is not required for their functionality. This includes sensitive details such as health data, social media profiles, and even biometric information. As a result, users are increasingly becoming aware of the need for stronger privacy measures when interacting with mobile apps.
Why App Privacy Matters
The risks to app privacy are not just theoretical—they can have real-world consequences. The more apps you use, the greater the chance your data could be exposed to cyberattacks, identity theft, or unauthorized third parties. Here’s why app privacy is so important:
-
Personal Data Exposure: Apps may inadvertently expose your personal information to the public, putting your security at risk.
-
Identity Theft: Malicious apps can steal personal details such as credit card information or social security numbers.
-
Data Sharing: Some apps may share your information with advertisers or other third parties without your consent.
Protecting your privacy within apps is about more than just protecting your personal information—it’s also about safeguarding your digital identity.
Common Privacy Risks in Apps
1. Data Collection Beyond the Necessary
Many apps collect data that goes far beyond what’s necessary for the app to function. Some apps gather information such as:
-
Location tracking: Apps often track your location, even when you don’t need navigation services.
-
Contact lists: Certain apps may ask to access your contact list, even though they don’t need this data.
-
Browsing history: Some apps track your online activities to build a profile for targeted advertising.
Pro Tip: Always review the permissions requested by an app before downloading it, and deny any that seem unnecessary.
2. Third-Party Data Sharing
Apps often share your information with third parties like advertisers or marketers. This may include personal details such as your interests, location, and browsing habits. While some apps are transparent about these practices, many aren’t.
This creates privacy concerns, as third-party companies may use your data for purposes you didn’t intend or even resell it to other parties.
3. Unencrypted Data Transmission
Some apps fail to use encryption protocols when transmitting your personal data. This means that hackers can intercept your information while it’s in transit, especially on unsecured public networks.
When apps do not encrypt your data, it can leave you vulnerable to hacking, identity theft, and even financial loss.
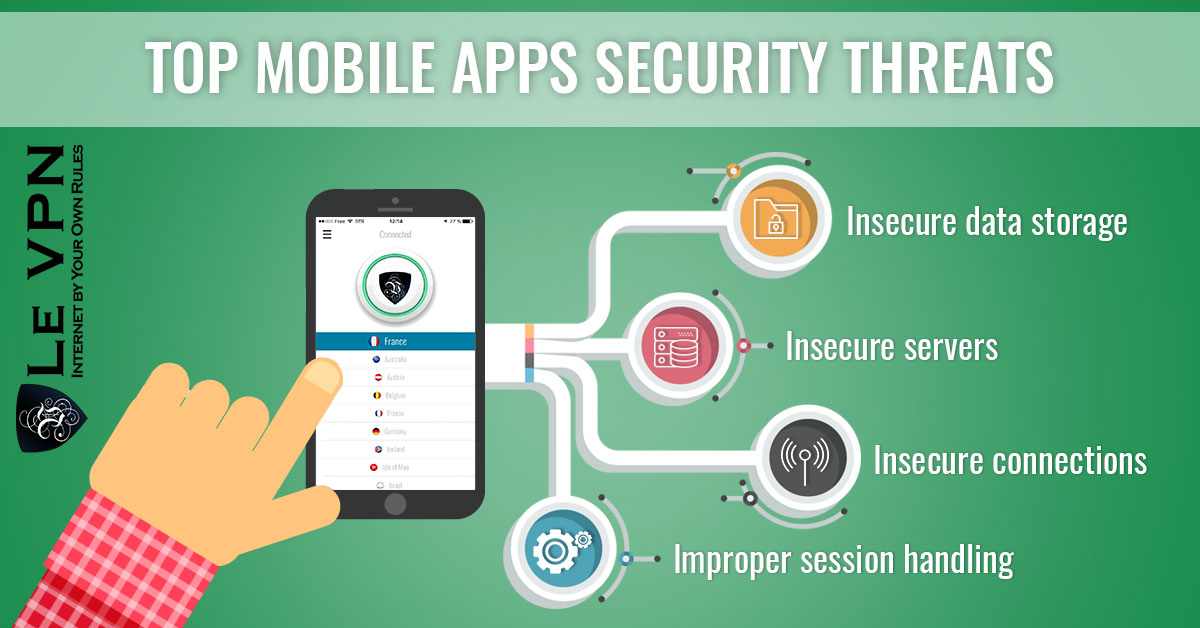
4. Insecure Cloud Storage
Some apps store personal information in the cloud. If these cloud servers aren’t secure, hackers can easily access your sensitive data. Many apps store passwords, credit card numbers, and health data, all of which can be exploited if not properly encrypted and secured.
Pro Tip: Be mindful of apps that store personal information in the cloud and ensure they use strong encryption measures to protect your data.
How to Protect Your Privacy When Using Apps
With so many privacy risks associated with apps, it’s crucial to take proactive steps to protect yourself. Here’s what you can do:
1. Limit App Permissions
Before installing an app, review the permissions it requests. If an app asks for more access than it needs, such as your contacts or location for a task that doesn’t require it, consider whether it’s worth granting those permissions.
Tip: On both Android and iOS, you can adjust permissions after installation by going to the app settings and disabling unnecessary features.
2. Use Privacy-Focused Apps
Consider using apps that prioritize user privacy. There are several alternatives to popular apps that don’t collect or share your data with third parties. Apps like Signal for messaging or DuckDuckGo for browsing are designed with privacy in mind.
These apps offer secure, end-to-end encryption, ensuring that your conversations or searches stay private.
3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your app accounts. By requiring both your password and a second form of verification (like a text message or authentication app), you make it much harder for attackers to access your data, even if they have your password.
4. Use a VPN
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) can help protect your data when you’re using apps over public Wi-Fi networks. It encrypts your internet traffic, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept your personal information.
Using a VPN ensures that your app activities are secure, even when browsing on less-secure connections.
5. Regularly Review Privacy Settings
Many apps offer privacy settings that allow you to control what data is shared and who can see your information. Regularly check the privacy settings in your apps to ensure you’re only sharing what you’re comfortable with.
Pro Tip: Review your settings every few months, as apps often update their privacy policies and features.

What Are the Legal Protections for App Privacy?
There are various laws and regulations designed to protect users’ privacy when using apps. Some of the most notable ones include:
-
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The EU’s GDPR regulates how companies collect, store, and process user data. It gives users greater control over their data, including the right to be forgotten.
-
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This law gives California residents the right to know what personal data is being collected and the option to opt out of data sales.
While these laws help protect users, not all countries have similar privacy protections. As a result, you must stay informed about the rules and regulations that apply to your data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can I know if an app is safe to use?
You can research the app’s privacy policy, check user reviews, and ensure it has strong encryption features. Avoid apps that ask for excessive permissions.
Q2: Can apps track my location without my consent?
Some apps can track your location even if you don’t actively use them. Always adjust your location settings and disable permissions for apps that don’t need your location.
Q3: Is it safe to store passwords in apps?
It’s safer to use a password manager app that encrypts your passwords. Avoid storing passwords directly in apps that don’t offer encryption.
Q4: How can I stop an app from sharing my data with third parties?
Review the app’s privacy settings and opt out of data sharing if the option is available. Also, avoid apps that require unnecessary permissions.
Conclusion
As apps continue to evolve, the importance of privacy and data security only increases. While most apps provide valuable services, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and understand the risks involved. By taking proactive steps to secure your personal information and being selective about the apps you use, you can protect your privacy and enjoy a safer digital experience.
Always remember to regularly review your app permissions, use privacy-focused alternatives, and stay informed about the latest privacy policies. This way, you can ensure that your data remains in safe hands.
Stay protected and keep your privacy intact as you navigate the digital world!